
Project Budget – What Is It and How to Effectively Plan It?
A project budget is a key element of any undertaking. It allows you to predict and control expenses, avoiding unexpected costs. A well-planned budget ensures control over the project and enables effective resource management. In this article, you’ll learn what costs to consider, how Time & Materials and Fixed Price models differ, and when financial assumptions need to be adjusted.
In this article:
- What is a project budget?
- Why do you need a project budget?
- What are the methods of project budgeting?
- What costs should be included in a project budget?
- How to plan a project budget?
- Project budgeting – summary
What is a project budget?
A project budget is a financial plan that specifies the anticipated expenses for the implementation of a project. It includes estimated costs of resources, materials, technology, and labor needed to achieve the objectives.
In practice, the budget serves as a control tool, allowing you to monitor expenses and adjust them as needed. It’s also the basis for assessing the profitability of the project and making financial decisions at every stage of its implementation.
Why do you need a project budget?
A project budget is essential because every commercial initiative must eventually be assessed to determine whether the costs incurred will translate into profits from its implementation, i.e., a return on investment (ROI).
The project budget as a management tool
A project budget is therefore a key management tool that allows you to control expenses, optimize the use of resources, achieve project goals, and provide relevant information to stakeholders.
Controlling expenses, i.e., monitoring costs incurred in real time, allows you to avoid unforeseen financial shortfalls. The budget should be updated, verified, and adjusted multiple times throughout the project, because this is the only way to keep expenses under control. Unexpected costs during the course of the project may force changes to the project scope, the implementation of specific system elements, or project-related process optimization. Without ongoing control of the project budget, the Project Manager won’t know that these actions should be taken.
Keeping the budget under control is one of the measures of project success. It provides a foundation for discussions with investors, clients, and management regarding what is needed and when to complete the project. Optimizing the use of resources allows for the effective allocation of funds to individual stages of the project.
What are the methods of project budgeting?
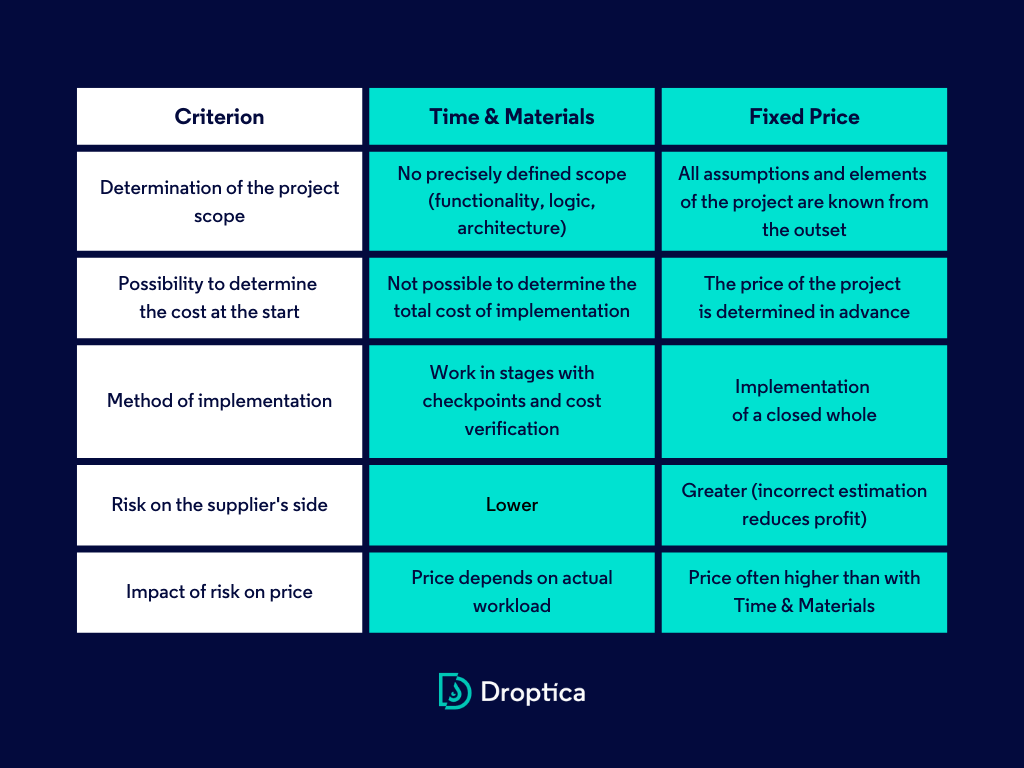
The most common methods of project budgeting in software development companies are hourly billing (Time & Materials) and Fixed Price billing. Each of these ways carries its own specific risks.
What characterizes hourly billing?
Hourly billing is more commonly used for projects where the scope, such as the functionality, logic, or overall architecture, hasn’t been clearly defined yet. In such situations, it isn’t possible to determine the total cost of the project. Nevertheless, there should be specific checkpoints where the costs incurred are summarized, the project budget is verified, and the next stages of work are determined. Then, the cycle repeats.
What is fixed price billing?
Where a project is a closed whole, all assumptions are predetermined and all its elements are known, a Fixed Price model makes sense. It’s a predetermined price for the delivered product. From the supplier's (software development company) point of view, such a project carries a higher risk because if the labor intensity is miscalculated, the cost reduces the contractor's profit. For this reason, in order to cover the potential risk, the final price of the project is often higher than in the Time & Materials billing model.
Reality shows that it’s very rare to be able to predict all the circumstances and assumptions of a project, so even when working in the Fixed Price model, budget adjustments are usually necessary during the course of the project.
What costs should be included in a project budget?
The IT project budget is not just about development, i.e., the work of programmers. This approach is a common mistake in estimating costs. Below are other areas that are worth considering when planning expenses.
Project materials and software licenses
Project costs also include materials used, e.g., licenses for specific software necessary to complete the project – assuming that licenses for standard software used on all projects are already included in the hourly rate.
Communication and project management
There are no projects that don’t require web development team meetings or contact with the client to demonstrate the progress of work. The project budget should cover the time spent on all communication activities and additionally include a buffer for additional, unforeseen conversations that the client may expect.
Requirements analysis and project planning
The budget should also include time for research and analysis of client requirements, which is necessary for a proper understanding of the business and technological needs of the project. This is particularly important so that the approach to the project doesn’t have to be corrected over time as a result of misunderstanding the customer's objectives.
Testing and corrections
Testing the project at all stages of implementation is another item that takes up the team's time, but is essential for early detection of errors. After all, none of us would want to deliver a low-quality project to the client.
After testing, corrections may be necessary, so it’s advisable not to use the entire production budget at the first iteration stage of the task. A reserve should be kept for error correction, verification of assumptions, and implementation of any fixes.
Buffer for risks and unforeseen work
When determining the project budget, it’s also necessary to include a buffer for unforeseen circumstances, the implementation of risky activities, or tasks with an imprecisely defined scope. Such elements appear in the implementation of every project, only their scale may vary.
Maintenance and post-launch costs
When budgeting for web projects, it’s also worth remembering the post-production costs, i.e., the maintenance of the website after implementation. This budget should include the cost of the infrastructure necessary for the website to function, i.e., servers, domains, and security certificates. An additional cost will be updating the website system to maintain its safety. Another important item is the expenditure on website marketing and SEO positioning.
How to plan a project budget?
To plan your budget effectively, it’s worth following a few key rules.
- Estimate the total cost of the project. Identify all components of the budget and assign realistic values to them, taking into account both direct and indirect costs.
- Base your estimates on data from completed projects. Analyzing the costs of completed projects allows you to avoid underestimating expenses and makes it easier to predict potential risks.
- Include a budget reserve. Prepare a financial buffer of 10 to 20% of the total budget to avoid problems in case of sudden changes.
- Set spending priorities. Identify the key elements of the project and focus on financing them first.
- Identify potential savings. Check which elements of the project can be optimized or implemented using cheaper methods without compromising quality.
- Align your budget with your schedule. Ensure that expenses are spread evenly over time and correlated with key project milestones.
- Ensure financial transparency. Keep accurate records of expenses and communicate them to your team and stakeholders to avoid misunderstandings.
- Monitor and update your budget regularly. Periodically checking expenses and adjusting funds to actual costs helps you avoid overruning your budget.
- Use financial forecasting methods. Use analytical tools to predict potential deviations from the budget and respond to them in a timely manner.
Project budgeting – summary
Effective project budget management is the key to the success of any venture. Appropriate budgeting methods, consideration of all costs, and ongoing financial control help avoid financial problems.
When planning a budget, it’s worth basing it on historical data, realistically estimating costs, and regularly monitoring expenses to ensure that the project is implemented according to the planned schedule and budget.
At Droptica, we use an approach based on realistic estimates, regular verification of assumptions, and transparent communication with the client. It allows us to effectively manage the budget and scope of work, maintaining a balance between cost control and the quality of solutions provided by our Drupal agency.











