
How to Choose Drupal Hosting? Avoid Costly Mistakes
Which hosting to select for Drupal? This is one of the most frequently asked questions among people starting their work with this CMS. In this article, I’ll explain what to pay attention to when choosing Drupal hosting and provide a brief overview of available options – based on 15 years of experience implementing Drupal for clients from Poland and abroad. I invite you to read the post or watch the episode from the Nowoczesny Drupal series.
In this article:
- When is simple Drupal hosting enough?
- Parameters to determine before choosing Drupal hosting
- Technical requirements – Drupal 10 and Drupal 11
- Three main types of Drupal hosting
- Shared hosting – a solution for simple projects
- Hosting platform – automation for actively developed projects
- Server with root access – full control for advanced systems
- CDN as a Drupal hosting budget saver
- Uptime, scalability, and migration between hosting providers
- Overview of Drupal hosting offers
- How to choose Drupal hosting? Summary
When is simple Drupal hosting enough?
Before we move on to detailed analysis, it’s worth answering a fundamental question: does the choice require deeper analysis at all? Drupal is a system written in PHP, using a MariaDB or similar database. This configuration is standard in the hosting industry, so for projects without special requirements and low traffic, the choice can be simple and intuitive.
In such situations, it’s enough to choose a reliable provider and install Drupal. Even if the configuration isn’t optimal, the system can be easily moved to different hosting. Drupal is fully portable between environments, which gives you great freedom when changing infrastructure.
However, if you’re running or planning a complex project, have a system with high traffic, or need precisely tailored infrastructure, the rest of this article will be crucial for you. I’ll present an extensive overview of options that will help you make an informed decision tailored to your project’s specifics.
Parameters to determine before choosing Drupal hosting
Before choosing hosting, it’s worth analyzing two key parameters: system complexity and its load.
System complexity verification
Complexity includes the number of data types, their mutual relationships, and the scale of content. For example, a simple blog with several content types is a completely different situation than a portal with 20-40 different data types connected by complex relationships.
The scale of stored data is also important – are we talking about 100-200 entries, or perhaps hundreds of thousands or even millions of records in the database? The analysis should also include the use of additional services, such as Apache Solr for search, Redis for caching, or Drupal integrations with external systems. The more complex the system, the more attention should be paid to selecting appropriate hosting infrastructure.
Server load analysis
The second key parameter is server load. In a typical web service, load is generated by two groups: users visiting the site and editors managing content in the CMS. User traffic can range from several dozen visits per day to hundreds of thousands or even millions.
Content editing looks similar. One scenario is a marketing specialist publishing one blog post per week. Another is 10 editors, each adding 20 or more pieces of content daily, then editing and correcting them, generating new queries to the server with each save. Additional sources of load can be interactive functions, such as a comment system or user forms.
Writing down usage scenarios – both current and planned – allows you to precisely match hosting resources to the actual project needs. Such analysis is the foundation of a conscious choice of hosting solution.
Technical requirements – Drupal 10 and Drupal 11
After determining the system characteristics, it’s worth checking Drupal’s technical requirements. The distinction between Drupal 10 and 11 is important because Drupal 10 has support until 2026 and many sites will remain on this version for some time. The main differences between versions concern required PHP and database versions.
Most modern hosting providers support PHP 8.1 and 8.3 without problems. The situation is similar with databases, although there are exceptions – some cheaper shared hosting may not support the latest MariaDB versions required by Drupal 11. The full list of technical requirements is available in Drupal’s official documentation.
It’s worth checking these requirements before deciding on hosting to avoid unpleasant surprises after purchasing the service. This is especially important when choosing cheaper shared hosting, where PHP and database version updates may be delayed compared to the latest standards.
Three main types of Drupal hosting
Drupal hosting offers can be divided into two main categories: hosting without Root access (main Linux system administrator) and hosting with full access. The first category is additionally divided into two subgroups.
- Shared hosting is the most popular service, in which the provider places dozens or hundreds of client accounts on one server.
- Platform as a Service is a dedicated solution combining a web server, PHP support, and database with additional features – Git integration, the ability to create multiple system instances for testing, or deployment automation.
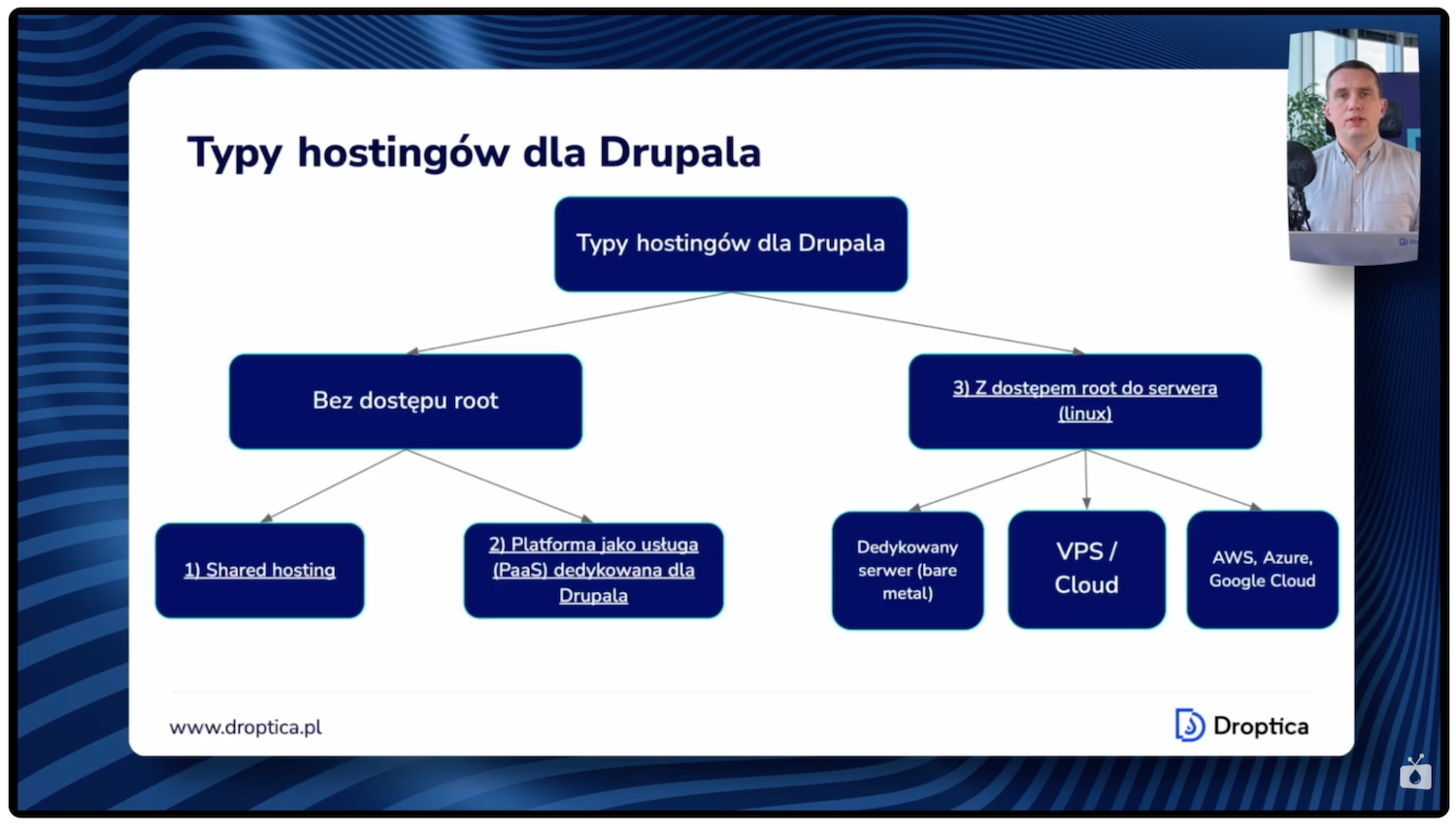
In the rest of the article, we’ll analyze three main types of hosting: shared hosting, hosting platform, and server with Root access. We’ll discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each solution and determine which projects they work best for.
Shared hosting – a solution for simple projects
Shared hosting will be an ideal solution for simple projects, such as a company website with fewer than 50-100 subpages, rarely edited and without high traffic. In such cases, you can choose practically any provider without deep analysis of technical parameters.
Advantages of shared hosting
The main advantage of shared hosting is low price. Offers usually start from around 600 PLN per year (about 50 PLN per month), with the first year often promotional and costing even half as much. This makes shared hosting the most economical option for small projects and companies starting their journey with Drupal.
Setting up the environment usually takes a dozen or so minutes – just fill out a form, make a payment, and the hosting account is ready to use. The server, PHP configuration, and database are already prepared, all that remains is uploading Drupal files and database or installing the system from scratch.
Another advantage is an intuitive management panel that makes it easy to add new domains and subdomains. An important advantage is the ability to host multiple sites on one account – functionality particularly useful for agencies and companies managing multiple projects simultaneously.
Disadvantages of shared hosting
The main disadvantages of shared hosting are limitations in configuration and available resources (processor, RAM). Problems may also appear with running CRON jobs or other background processes. Projects needing specific PHP settings or advanced automated tasks may prove too demanding for this type of hosting.
Shared hosting performance can be variable due to the resource sharing model. One server handles accounts of dozens, and sometimes hundreds of clients. If other accounts don’t generate high load, the site works smoothly. However, when the server is overloaded by other users, it can affect your site’s performance.
In case of performance problems, it’s worth contacting the hosting company with a request to move the account to another server. Most providers offer this possibility, especially when you present specific problems. This is a simpler option than migrating to a completely different provider.
Hosting platform – automation for actively developed projects
Hosting platforms offer much more capabilities, especially for actively developed projects. If you’re deploying new functionality every week or every few days, need test environments, and work in a team of programmers, a hosting platform automates the entire deployment process.
Advantages of hosting platforms
A platform account is always integrated with a Git repository. Just push changes to the appropriate branch or create a new tag, and the system will automatically deploy them to production or a dedicated test environment. Various automations can be defined as part of the deployment process. Although a similar configuration can be created on shared hosting with SSH access, it requires independently writing and later maintaining scripts, which takes additional time.
Platforms often rely on Docker images, which enables easy addition of services such as Apache Solr, Redis, or Memcache. Scaling the project and expanding functionality is much simpler than with traditional hosting. The ability to instantly launch a development environment identical to production significantly reduces the risk of errors during deployments.
Disadvantages of hosting platforms
The main limitation of hosting platforms is certain configuration restrictions. Although they usually offer wide customization possibilities, in the case of very complex systems with high load, it may turn out that not all PHP or database parameters can be changed according to needs. An additional challenge is price – for services requiring large resources, costs can be significant.
If the monthly platform cost is in the range of 200-1000 euros, it’s worth analyzing whether a dedicated server set up from scratch wouldn’t be more cost-effective. Such analysis should include the time needed to prepare the server and the costs of its later administration. Comparing all factors allows you to make an optimal decision.
An important difference compared to shared hosting: one account on the platform is one site, one system. For multiple projects, you need to pay for each one separately. For agencies managing multiple projects, costs can grow quickly, which requires careful economic analysis.
Server with root access – full control for advanced systems
The third option is servers with full root access – VPS servers, Cloud, or traditional dedicated servers (although the latter are used less and less often). The main advantage is full configuration freedom and virtually unlimited environment customization possibilities.
Advantages of servers with full access
On such servers, you can use Docker or Kubernetes, choosing any container images – publicly available and your own, created for a specific project. Both simple configurations and very complex architectures are available.
A server with full access also enables implementation of custom CI/CD processes (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment). All specific operations during deployment of a new system version can be tailored to individual needs. This flexibility is invaluable in the case of very complex projects requiring non-standard solutions or integration with many external systems.
Disadvantages of servers with full access
As for disadvantages, additional resources are definitely necessary here, such as time or budget related both to server maintenance and its initial configuration. In situations where the environment is complex, migration to different hosting in the future will also be more time-consuming, and this should also be included in the analysis of hosting options.
It should be remembered that your own server means not only greater control but also greater responsibility. Continuous monitoring, security updates, backups, and quick response to failures are necessary. Therefore, it’s worth considering whether the company has appropriate technical competencies in the team or budget for an external company dealing with server administration.
CDN as a Drupal hosting budget saver
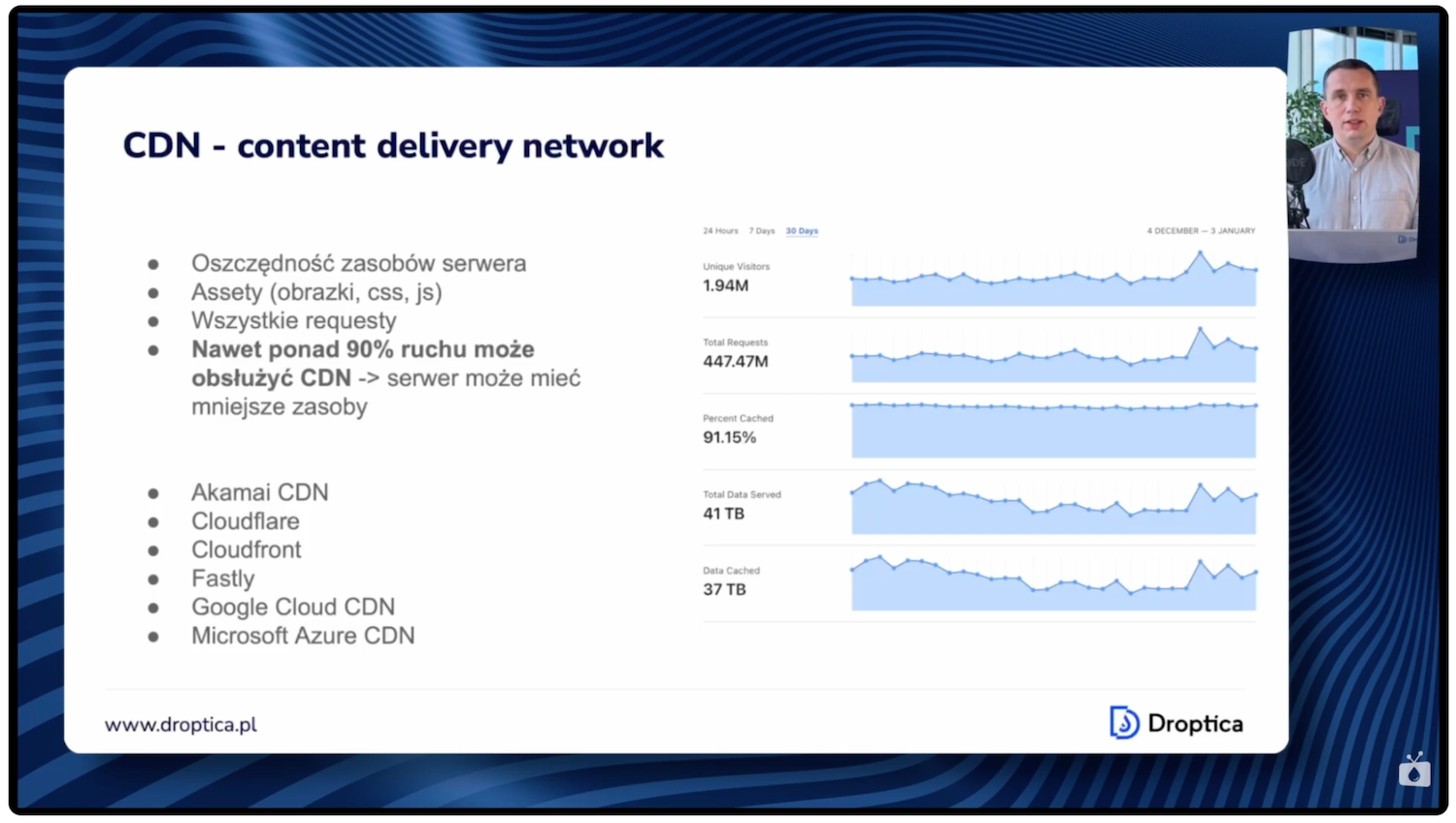
When analyzing hosting options, it’s worth considering CDN (Content Delivery Network) implementation, which can significantly reduce required hosting resources. An example from one of our projects shows the scale of possible savings: in 30 days, the system handled over 400 million requests from 2 million unique users, with over 90% of them served by the CDN server (in this case Cloudflare), not the hosting server.
The effect is impressive – required hosting server resources can be about 10 times smaller because only 10% of all traffic reaches the server directly, and the remaining 90% reaches users from CDN servers. This means huge savings both on server resources and bandwidth, which directly translates to lower monthly costs.
CDN for simple company websites
Even for simple company websites, it’s worth implementing CDN, especially since basic accounts are free. However, one limitation should be remembered: pages with forms in Drupal have caching disabled by default, so they won’t be delivered from CDN but directly from the hosting server.
This can be worked around in various ways, but by default every page with a quote request form or comments won’t be cached. It’s worth remembering this when designing site architecture and considering alternative solutions, such as placing forms in dynamically loaded modals, to maintain the benefits of caching entire pages.
Uptime, scalability, and migration between hosting providers
Beyond the basic hosting types, several operational factors can significantly impact your Drupal site’s long-term success. Understanding uptime guarantees, scalability options, and migration processes helps you avoid common pitfalls and ensures your hosting can grow with your project.
Uptime guarantees
Most hosting providers present server uptime data on their sites – usually these are values on the order of 99% or 99.9%. However, it’s worth checking the terms and conditions because they often don’t contain actual future uptime guarantees. If your system requires guaranteed uptime at 99% or higher, you should ask about a dedicated service with SLA (Service Level Agreement) guarantee.
Such guarantees are usually associated with signing a contract for one or two years and higher costs than in the standard price list. Not every provider offers such an option – especially in the shared hosting segment. SLA guarantees are usually available in more expensive hosting platform packages or with dedicated servers.
Resource scalability
Another aspect worth attention is hosting scalability, meaning the ability to dynamically change available resources (processor, RAM). This is especially important for projects with seasonal character, where user traffic significantly increases during certain periods of the year. Shared hosting usually doesn’t offer dynamic resource scaling options.
Hosting platforms and cloud servers enable scaling, but it’s worth getting to know the details of this process thoroughly. A key question concerns whether parameter changes require interruption in site operation – and how long such interruption might last (one minute, two, or perhaps an hour). This information allows you to properly plan periods of increased traffic and avoid downtime at critical moments for the business.
Migration between servers
It’s also worth considering potential migration between hosting providers. System requirements may change – the project may become more complex, traffic may increase, or new functionalities requiring better infrastructure may appear. Therefore, it’s worth getting to know the migration process to another provider already at the hosting selection stage.
The more complex the system, the more complicated and time-consuming the migration process can be. You should make sure you have easy access to all data, backups, and the ability to export configuration. Some hosting platforms offer tools facilitating migration, which can be an important argument when choosing a provider.
Overview of Drupal hosting offers
The following overview of hosting offers is based on experience gathered at Droptica and suggestions from users of the Drupal PL group on Facebook. It’s worth emphasizing that this is not a recommendation of specific providers – each project has individual needs requiring separate analysis.
If you need a Drupal hosting recommendation tailored to your project’s specifics, feel free to contact us – we’ll help you choose the optimal solution.
Shared hosting
Shared hosting is a solution particularly suitable for smaller projects, especially company websites. A Drupal system will work on practically any shared hosting, so choosing a specific provider can be quite flexible.
When choosing shared hosting, it’s worth paying attention not only to price but also to technical parameters: PHP and database versions, memory limits, SSH access, and technical support quality. Opinions of other Drupal users about the given hosting may also be useful.
Hosting platforms
Several main players stand out among hosting platforms. Acquia doesn’t publish its prices publicly and requires individual contact. Their offer is mainly aimed at larger systems requiring high performance and significant resources.
Other platforms, such as Upsun (formerly Platform.sh) and Pantheon, offer packages for projects of various sizes. When choosing a platform, it’s worth analyzing not only prices but above all the range of offered functionalities. The main advantage of hosting platforms is that they combine the capabilities of VPS or dedicated servers with a ready, fully configured environment. This eliminates the need to hire a specialist for server configuration and maintenance, which should be included in the overall cost analysis.
Upsun (formerly Platform.sh) is particularly popular among medium-sized projects, offering a good balance between price and functionality. Each platform has slightly different capabilities and pricing models, so it’s worth comparing them thoroughly in terms of your project’s specific needs.
VPS and cloud servers
Servers with full access include traditional VPS, cloud servers, and dedicated ones. In our experience, we most often use Hetzner for cloud servers and AWS for larger, more demanding projects.
Currently, most of our clients use hosting platforms – mainly Upsun (formerly Platform.sh), but also Acquia and Pantheon. We host large projects with high traffic most often on AWS or Hetzner. Smaller sites, especially those based on Droopler, run on shared hosting.
AWS offers the greatest flexibility and the widest range of services, but also requires the most technical knowledge. Hetzner, on the other hand, offers very competitive prices with solid performance, making it a popular choice for medium-sized projects. Cloudflare also appears as an option for projects requiring advanced DDoS protection and global content distribution.

How to choose Drupal hosting? Summary
For simple projects, such as small company websites, the choice is simple – any shared hosting for about 50 PLN per month is enough. There’s no need to complicate the choice or overpay for advanced features that won’t be used.
In the case of more complex systems, the decision-making process requires analysis of several key factors: what makes the system complicated, what the load is or will be, what the technical requirements are, whether uptime guarantee is needed, whether scaling option is required, what budget is available for hosting, and whether resources (time or budget) are available for server administration.
After analyzing these parameters, you can choose the appropriate type of hosting: shared hosting, hosting platform, or server with full access. The next step is reviewing specific provider offers and choosing a solution that best fits the project’s specifics.
If you don’t have time for independent analysis, we offer help in choosing the optimal solution. We can also configure a dedicated VPS or cloud server tailored to your system. Feel free to contact us – we’ll help you choose Drupal hosting.











