
What is Technical SEO and How To Do It for Your Website
Search engine optimization is a complex process consisting of many smaller and bigger activities. They are all aimed at optimizing your website so that it could be better visible for search engines, and thus more often visited by your prospects. For these purposes, the crucial practices to apply are the ones related to technical SEO. We’ll explain to you this process and its elements. We’ll also show an easier way for optimizing a Drupal website with a Droopler tool.
Technical SEO and its benefits
Technical SEO is a set of optimization activities focused on a website’s infrastructure. Making it better organized and easier to understand helps the search engine crawlers seamlessly interpret and index a particular page. If you have great content but don’t pay attention to technical SEO, the robots won’t be able to find your website, not to mention showing it to the broader audience.
The search engine crawlers look at many different factors like the loading speed of a website, its structure, and mobile-friendly design. Mastering these elements will:
- help your web page rank higher in SERP (Search Engine Results Pages),
- keep your website up and running,
- make it clear and easy to use for your visitors.
10 SEO factors to focus on
As we’ve already mentioned, there are loads of factors that matter for technical SEO. We’ll analyze the top ones for you so that you don’t feel lost in this complex topic and know where to begin. But before we start explaining these elements, we’ll show you a must-have tool that identifies errors on your website that may affect your SEO.
Google Search Console
This tool lets you get to know how Google Search sees your pages. It also detects the issues on them and sends you alerts so that you could quickly fix the problems. To start using Google Search Console, follow these handy setup guidelines. After completing them, you’ll be ready to take advantage of the rich option this solution provides. Now, we’ll look at two of them.
The Index Coverage report
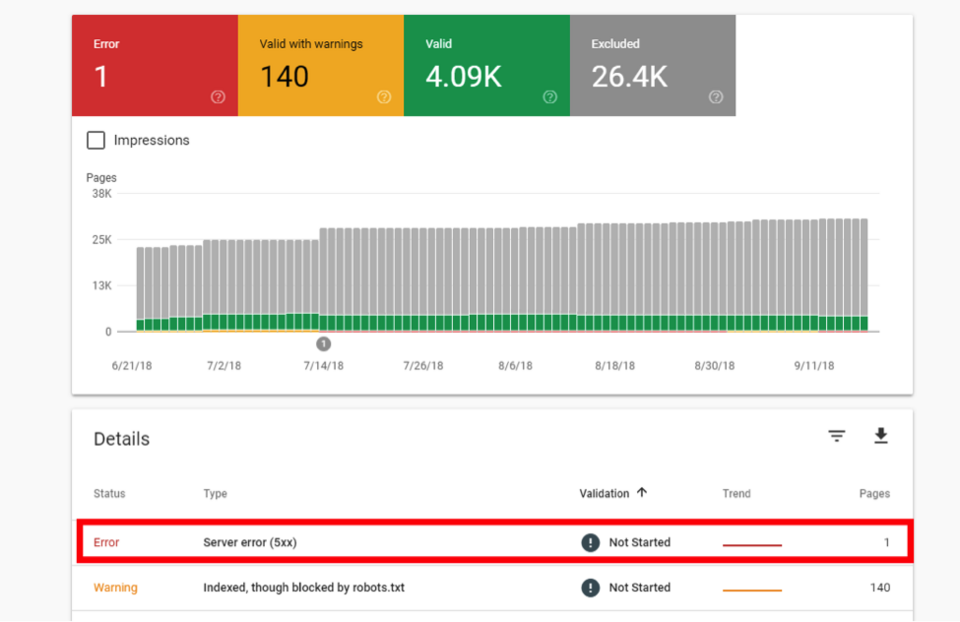
Using this report, you can see which of your pages have been indexed properly by Google robots and which haven’t because they encountered some problems. In such a situation, you’ll get the Error status and have a possibility to scroll down to the Details section to discover problems grouped into several categories, like:
- Server error (5xx) - meaning that your server returned a 500-level error,
- Redirect error - informing that redirect chain was too long, there was a redirect loop, empty or bad URL in the redirect chain, or the redirect URL overrun the maximum URL length,
- Submitted URL not found (404) - you submitted for indexing an URL that doesn’t exist.
Source: WordStream
When you click on the chosen error, you’ll get the list of URLs of affected pages. This way, you know both the details of the issue and its location.
URL Inspection tool
At the top of Google Search Console, you can find a search bar. Type the page’s address that you’d like to inspect. You’ll receive information about Google’s indexed version of that page. Thanks to it, you’ll know whether:
- URL was successfully indexed and can (Google uses this verb as it doesn’t consider temporarily blocked URLs or security issues) appear in SERP,
- URL is on Google, but there are some issues,
- URL isn’t on Google because of indexing errors.
In all of these cases, you’re able to get to know more details.
Now that you know the tool that can support your optimization efforts, let’s go on to the technical SEO checklist.
1. SSL certificate
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) website protocol is a ranking signal as Google wants to enhance security on the web this way. This protocol ensures that the data sent between a site and a browser is safe as it keeps this communication private. To use HTTPS, you need to obtain the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate. You might have done it before the website launch. However, it’s important to always keep it valid. Losing the certificate, even for a moment, can affect the website’s visibility.
You can display information about the SSL certificate from every place on the website. Here we see it on our Drupal development landing page.
2. Robots.txt file
The Robots.txt is a simple text file - an instruction for the web robots on how to crawl pages on your website, and which of them to omit. To check how your Robots.txt file looks, type:
http://yourdomainname.com/robots.txt
It’s also possible to test the file for errors, write or edit something in it, using the robots.txt Tester from Search Console.
Robots meta tag
It’s a piece of code that you can place in the head section of a chosen page. Using it, you can instruct robots f.e. to crawl the page but don’t show it in the search results or don’t follow the links on the page. In the Google Search Central, you can find detailed guidelines on what to put in the robots meta tag for a given purpose.
3. Site structure
Site structure is important both for the users and the search engine robots. The first ones will stay longer on your web page if the places they want to reach aren't too many clicks away from the home page. For the second ones, you need a clear page construction so that they could easily crawl and index all your website’s pages.
Site structure refers to how your site’s content is organized (grouped and linked) and presented to the user. The web page construction should be hierarchical where at the top of it there is a home page and then 2 or 3 levels of other pages.
Here are some more elements to keep in mind:
- Categories - make sure they have similar sizes so that it could be easy to browse each of them.
- Internal links - include them on every page to build bridges between different parts of your website.
- Avoiding “orphan pages” - pay attention not to create pages without any internal links directing to them.
Sitemap
To make it easier for the crawlers to navigate through your website’s structure, remember to create and regularly update (as you add new pages) an XML sitemap. It’s a file with information about the pages, videos, and other data on your website, as well as the relationships between them. The sitemap informs the robots how your web page is organized and helps them crawl it more efficiently.
With Search Console, you can test and add your XML sitemap. To do so, click Sitemaps under Index in the side panel. There you can also see the already submitted sitemaps.
4. URL structure
All URLs should have a logical and consistent structure so the visitors could know where exactly they are on your website. As Google cares about user experience, they also recommend creating friendly URLs in their Search Engine Optimization Starter Guide. The right URL should be possibly short, have lowercase characters, words separated with the hyphens, and target keywords.
A clear URL address of our Drupal support landing page
5. Meta tags
These elements are the snippets of HTML code that help search engines by providing significant information about your website. We’ve already described the robots meta tag which explains the robots how to crawl a chosen page. But there are also other important meta tags you should properly optimize.
Meta title
It’s a page title that search engines display on their results pages. According to Google, it should represent and describe every result in the best way and clearly show the reference to the user's query.
Below you’ll find a few guidelines for a good meta title.
- Create a unique title tag for every page.
- Keep it concise, but descriptive.
- Make sure the title is related to a H1 tag of a particular site.
- Contain your target keyword.
- Use from 55 to 65 characters.
Meta description
The text included in this tag is located under the meta title on the search results page. It should briefly and relevantly summarize what a chosen page is about. Like in the case of a meta title, its content needs to be unique for each page and contain a target keyword. The proper meta description’s length is from 120 to 160 characters.
6. Structured data
Structured data is information written in the code, visible to the search engine crawlers, that you can add to your website. Most structured data uses Schema.org vocabulary. Thanks to this data, the robots can easier understand the context of individual subpages of the site. It can result in better presentation of your listings in the search results, f.e. in the form of featured snippets (special boxes where the descriptive element comes first, and the URL and title - second).
7. Website speed
It’s one of the most crucial factors that affect your website's ranking position. As we’ve already mentioned, Google cares about the user experience. When the website loads faster, the visitors will probably stay on it which is valuable information for the search engine. It’s possible to check your site’s loading speed with the PageSpeed Insights tool.
To enhance the website speed, you can:
- test and improve the server response time,
- upgrade your CMS and all its plugins or modules to the latest version,
- optimize the size of the images, CSS and JS files,
- minimize the number of redirects and eliminate the redirect loop.
8. Broken links and redirects
While encountering broken internal links, the Google robot may have problems finding and crawling the pages of your website. You can perform the check for damaged links using SEO tools like Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, or Semrush.
Having broken links, you can use redirects to let the users still access the searched content but under its new link. Redirections are helpful, but keep in mind that too many of them can slow down your website’s loading speed.
9. Canonical URLs
Canonical URL informs Google that this is the version of a page it should consider while indexing your website. It also helps distinguish this site from the ones that duplicate its content. To take advantage of this solution, you need to add the tag like here:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/dresses/green-dresses" />in all pages and blog posts on your website.
10. Responsiveness
It is an important factor for your page’s ranking as Google introduced mobile-first indexing a couple of years ago. Now they’re ranking mobile websites using their mobile content. That’s why the desktop version of your website should be properly accessible on mobile devices.
Regarding the user experience, your page should display the right way on tablets. There are different tools for testing website responsiveness. You can also check the Page Experience report in Search Console to get to know more about your current website’s mobile usability.
Website search engine optimization with Droopler
If you decide to build your website in Drupal, thanks to its numerous modules, you’ll have access to many tools for technical SEO purposes. The solution having all the useful modules out of the box is Droopler, a free open-source website builder based on Drupal CMS. Let’s take a closer look at the options it provides.
Page optimization
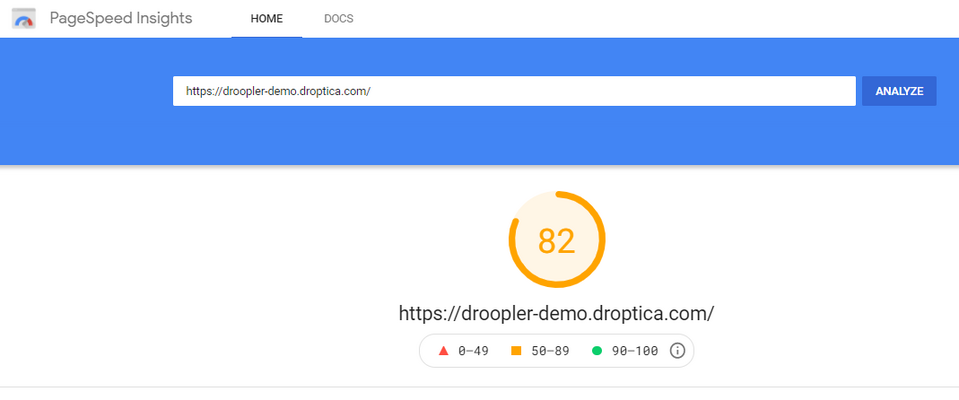
Droopler contains the Advanced CSS/JS Aggregation (AdvAgg) module which improves the websites’ frontend performance. It reduces styles and scripts and makes sure the page loads as fast as possible, both from the users’ and Googlebots’ perspectives. Below you can see the speed test result from PageSpeed Insights for the website built in Droopler.
Lazy-loading of images and iframes
Lazy-load is another module that helps Droopler websites achieve high scores in Google PageSpeed insights. Thanks to it, the page images aren’t loaded until the users scroll to them. This way, they don’t all upload at once.
Internal links, friendly URLs and redirects
Droopler has three modules related to links and page addresses. The first one, the Linkit module allows you to conveniently link both internal and external content. You just type a few words contained in the title and the tool suggests the target page.
The second module, Pathauto, automatically generates URLs based on the pattern you defined. And the last one we’d like to mention here is the Redirect module. It’s used for setting the redirects from one page to the other. It also has a handy option - Enforce clean and canonical URLs - which imposes using one main address for a site. Thanks to that, Google sees it only once, without duplicates.
A quick way for adding meta tags
The Metatag module enables you to easily set meta titles and descriptions for search engines and the Open Graphs meta tags for Facebook, LinkedIn, or Twitter. The second one lets you control how content displays after it is shared on social media. Using this module, you can define meta tags individually for every type of content.
There are also advanced options in the Meta Tags section that allows you to add the Robots meta tag and Canonical URL.
Droopler also has the Schema.org Metatag module that extends the Drupal project we mentioned above and enables displaying structured data in the head of pages.
Another module supporting your SEO efforts is the Simple XML sitemap for building sitemaps. Additionally, when a website has many subpages, the tool divides the map into several parts so that Google could correctly process it.
Features of a CMS for easier optimization
With a solid technical SEO, the search engine robots will easily understand your website and all its pages. It’ll result in indexing them and providing your site a high ranking position. Before it happens, you need to focus on optimizing different elements such as meta tags, URL structure, and page speed. Fortunately, some CMSs, like Drupal together with its distribution Droopler, offer quite a few tools that simplify this process.









