UI vs UX Design - Difference, Definitions, and Tasks of Designers
Behind the success of a digital product are many people handling design, analytics, programming, and testing. Today we'll take a closer look at one of the first steps in creating a digital product, which is UX and UI design. At this stage, the work mainly focuses on the client's business goals and ensuring that the product develops in line with current trends. What's the difference between User Interface and User Experience design?
What is UI design?
User Interface design is about designing all graphic elements, regardless of whether it's for a website, a device control program, or a mobile application. UI design covers icons, widgets, modals, buttons, the look of the navigation, and all the elements that allow us to move around a user interface. The designer uses these elements to build a graphically consistent product.
The graphic consistency of any digital product is essential for several reasons. The first and most obvious one is the visual appeal of our product. However, not everything is about looks. The product must have a set of unchanging rules that determine how the buttons work, what animations the clients will see when they hover over a given element, or what icon they will click on. To sum up, User Interface design is about designing all the elements with which the user comes into direct contact.
The tasks of UI designer
Many people would say that it isn't very complicated to design a few rectangles and arrange some photos. It's hard to disagree with it from a technical point of view, but building a well-functioning and aesthetically pleasing interface requires having specialist knowledge in addition to a sense of style.
UI designers not only take care of the proper use of logos and typography, but they also make sure that the design is consistent with how the whole brand wants to present itself. For the product to be well-prepared and meet all business goals, user interface designers work closely with UX designers. Through their work, they "enliven" the interface in terms of graphics and create final graphic designs that are forwarded to developers.
As the work of UI designers forms the creative part of building a product, they can introduce innovative and unconventional ways of displaying information and interactions between the user and the product they create. Their work also includes creating micro animations, which are small animations for graphic elements, increasing their attractiveness and helping users navigate them.
What is UX design?
User Experience design is one of the most important elements in the process of creating a new product. UX designers take part in the initial phase of product design. They are responsible for defining goals, not only for the user but also for the business.
Designers define problems and hypotheses, observe users and take into account all the business goals of the client in order to design the best possible product, taking care to meet the expectations of the group which this product is aimed at.
The common mission of UX design is to serve the user and make digital products improve the quality of life for people all over the world.
What does a UX designer do?
In the first stage, UX designer deals with the analysis of the data that they receive from the client or order for the project. It's also common to analyze the data from Google Analytics, which help to define who the target group visiting a given website is. This is very important because we'll think differently about a product for middle-aged men and when our target group is young women. The data provide answers to many basic questions that allow proceeding with the project further.
UX designers very often also conduct design workshops with clients, which are invaluable in defining the goals and functions that a given product or website is to achieve. These are several-hour-long meetings with representatives of various departments of the company, during which exercises are conducted aimed at learning about the strengths and weaknesses of the project, its requirements, and business goals. The facilitator, which is the person conducting such workshops, doesn't participate in them, but only leads the group in such a way that they develop the best model of functioning for their product.
Based on quantitative data (if the client has such data) and workshops, the UX designer makes further decisions about the next stages of research. There's a lot of research to be conducted, and choosing its direction depends on the budget, the time that the UX designer can devote to it, and the specific nature of the industry in which they are currently operating. One of the tests is to invite several users and give them goals to achieve so that they have to go through a given application. During this time, the UX designer takes a closer look at the users and checks whether all the goals set by the client are achieved, or whether some elements require additional consideration and processing.
When all the necessary data is collected, the UX designer designs product mock-ups, which are initial screens with application features, but not representing the final design. Such screens focus on the layout, choosing the right style of buttons in a given area, and establishing the data hierarchy. Thus, the designer focuses on correctly guiding the user through the product, so that all previously set goals are achieved.
When creating a given product or website, the work on them is never really finished. If the client launches any type of digital product on the market, they must be aware that the design trends, device technology, and user behavior are constantly changing. Therefore, UX designers monitor and study user behavior within a "living organism." One method is connecting user behavior monitoring programs. With these, you can later define problems and make the changes that'll improve usability. Thanks to this, you can easily react to changes in the market and continue product development. This method is also more cost-efficient than simply leaving the product to fend for itself for three or four years. Otherwise, you'll most likely have to design it from scratch.
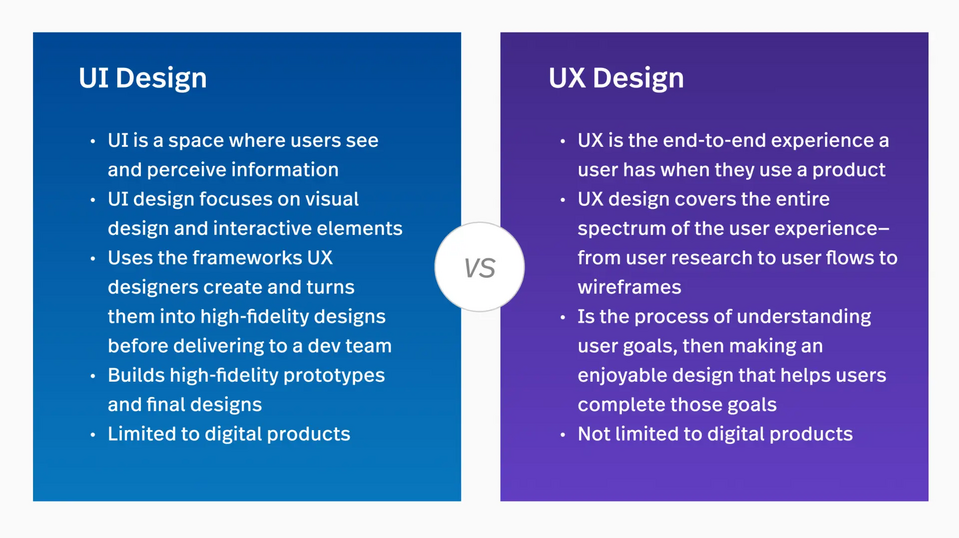
What's the difference between UI and UX?
We've already covered UI and UX design, but what are the differences between these areas? User Interface is the visual side of the design, while User Experience focuses on the user's journey and on the product's usability. UX design comes first because it's at this level that the most important questions are answered, such as who the potential clients are, what their problems are, and how to solve them.
Source: FullStory
UX designer involvement in the process of changes to the website or application is invaluable at every stage of its development. Sometimes there's no UI stage at all. Not all design tasks require the involvement of an interface designer. It may be enough to make changes that can be introduced using the existing design system - a document with a set of all principles and rules for using a given user interface.
UI vs UX – summary
A very frequently asked question is whether the UI is part of the UX. When UI designers think about the usefulness of their design, choose the colors so that the most important elements are clearly visible, and the typography is pleasing to the eye, in a sense they also think about UX. However, while the user interface may seem very aesthetically pleasing, it doesn't always do the job right. Therefore, UX designers work closely with UI designers. When a team or a person with knowledge in both of these areas works on the tasks, you can be sure that your product will be well-designed aesthetically, functional, and will meet the business goals.
At Droptica, we pay a lot of attention to design. Check out what exactly we do in terms of UX and UI design.










